The internal flora of people provides an excellent environment for the habitat and active reproduction of microorganisms that belong to the group of pathogens. The types of parasites in the human body are usually divided into two types: those whose presence is not felt and have virtually no effect on overall health, and those whose presence can be destructive. In the process of their life activity, they are capable of not only negatively affecting organs, but also releasing toxic substances that poison all living things.
General symptoms of infestation
When parasitic eggs or adult parasitic organisms enter the human body, there is an incubation period during which the parasitic infection may be asymptomatic. Signs of ectoparasites are immediately noticeable: allergic rashes, wounds, and itching appear on the skin. It is more difficult to identify endoparasites; parasitic diseases often have symptoms similar to other diseases. Primary symptoms are caused by toxins and are often perceived as a consequence of overwork and ignored. A signal for diagnosis is the appearance of the following symptoms:
- allergic reactions to waste products of parasites;
- anemia;
- headache;
- causeless sleep disorders;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- frequent nausea, abdominal pain;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the liver or enlargement of the organ;
- frequent causeless pain in joints and muscles;
- any long-term ailments not associated with other diagnosed diseases.
Types of human parasites
Given the high prevalence of human parasites, it is advisable to know the main types. It is also necessary to understand what symptoms accompany the presence of a particular parasite in the body.
Let's consider the general classification of parasites for which humans are the host:
Ectoparasites are dangerous because they are carriers of serious infectious diseases: typhoid, encephalitis, anthrax, trypanosomiasis and other ailments.
Ectoparasites, which can be contracted in exotic countries, cause enormous harm to health, so it is important to be especially careful when traveling.
The main types of protozoan parasites:
- Giardia leads to the development of dysbacteriosis, hypovitaminosis, intoxication of the body, disorders of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, anemia;
- amoebas provoke intestinal diseases and asthenia;
- toxoplasma can cause diseases of the eyes, brain, heart, nervous system, and are especially dangerous for pregnant women;
- Trichomonas lead to diseases of the reproductive system.
The listed varieties of protozoan parasites most often infect the human body. Infection with them can be accompanied by severe symptoms or occur without obvious signs.
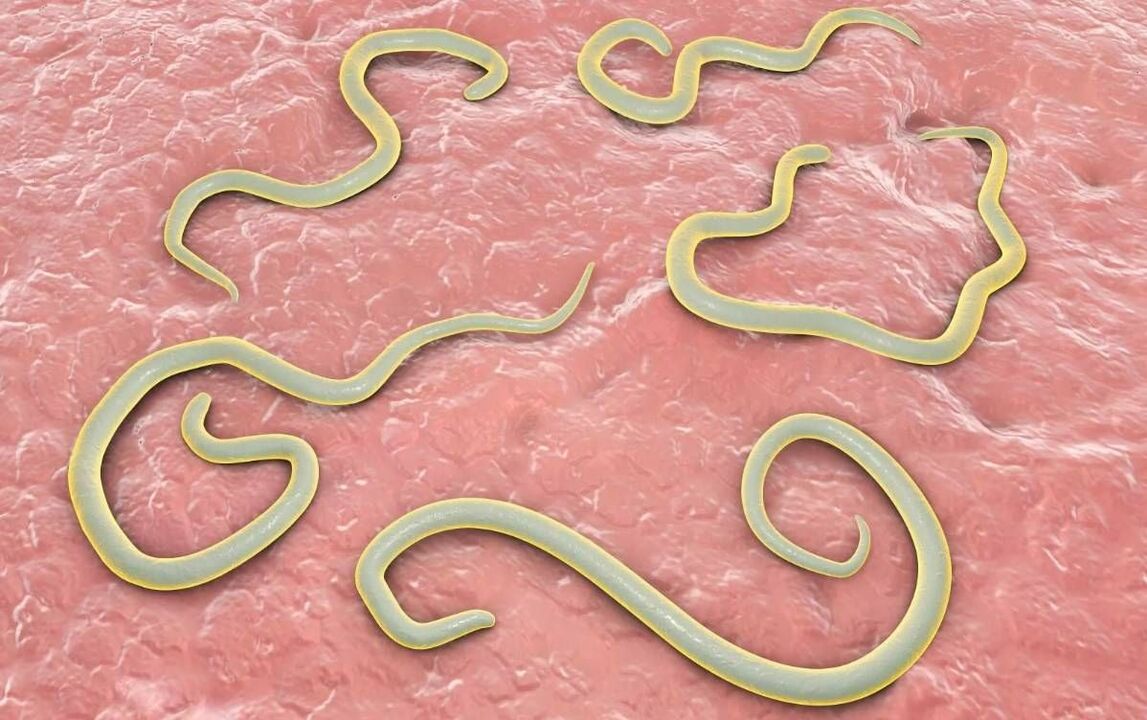
Helminths are the most common endoparasites, carriers of which are more than 80% of people. These worms, living in different organs of humans, lead to the development of dangerous chronic ailments. In the most severe cases, helminth infestation causes death.
Types of parasitic worms that affect people at any age:
Nematodes - this type of worm is often diagnosed in children and adults. This is due to the fact that they are easily transmitted from person to person or through contact with household items on which worm eggs remain, or through the consumption of poorly washed foods. Another name for nematodes is roundworms, since the body of these helminths when cut has a round shape. Their sizes vary from a few millimeters to tens of centimeters.
There are 45 species of nematodes that can live in the human body. The most common:
- pinworms are worms up to 1 cm long, living exclusively in the intestines, they lead to exhaustion, digestive disorders, and sleep disturbances;
- roundworms are dangerous parasites up to 30 cm long, migrating throughout the body, they provoke the development of allergies, asthma, anemia, dermatological diseases, and damage the integrity of organs. Roundworms can develop serious diseases;
- trichinella worms several millimeters in size, causing serious health problems: fever, swelling, dermatitis, allergies, stomach upsets;
- whipworms are worms with a body length of up to 4. 5 cm, which parasitize the intestines, causing the development of anemia, weakness, and intoxication.
Trematodes are helminths that have a flat shape. Another name for trematodes is flukes. It is due to the fact that all parasites of this group have suction cups on their body, which they attach to internal organs, absorbing useful substances, blood, and other body secretions.
To parasitize the human body, trematodes need to go through an obligatory development phase in the body of an intermediate host. Most often this is fish, so you can become infected with trematodes by eating fish meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment. The most common flukes:
- Siberian or cat fluke (opisthorchus) is a flatworm 1-2 cm long, it parasitizes in the ducts of the gallbladder, as well as the pancreas, liver, causing the development of ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and nervous disorders;
- intestinal eel (strongyloid) is a worm up to 2 mm long, infection with which leads to diseases of the digestive tract, asthma, anemia, allergies, asthenia, bronchitis, and infertility.
- Cestodes or tapeworms are a dangerous type of parasite, reaching tens of meters in length. To develop, they need to change an intermediate host, most often these are ungulates. Parasite larvae enter the human body if they eat contaminated meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment. The main types of tapeworms are: a wide tapeworm helminth several meters long, parasitic in the small intestine; it provokes diseases such as anemia, intestinal obstruction, digestive problems, asthenia; pork tapeworm is a worm up to 8 m long, infection with which leads to intestinal obstruction, cysticercosis, taeniasis; bovine tapeworm is a parasite up to 18 m long that provokes dangerous human diseases: anemia, exhaustion, intestinal obstruction, stomach upsets, allergies, problems with the nervous system; Echinococcus is dangerous for humans when infected with the larvae of this tapeworm, since when they enter the body, they quickly develop and form large tumors.
Trematodes are very dangerous. They spread throughout the body, causing multiple mechanical damage to organs, absorbing large amounts of blood and useful substances.
Classification of types of parasites in the human body
There is a division into true and false parasitism. Cases where the pest is not considered a human parasite and causes harm when it accidentally enters the body are classified as false parasitism. An example is insects and leeches in the nasopharynx or ear canals. Due to the risk of extensive damage and blockage of the respiratory tract, emergency removal of the pest is required. Treatment of true parasitism is mainly medicinal, depending on the type of pest.
Ectoparasites
In spring and summer, as well as early autumn, the peak activity of ectoparasites occurs. Organisms that parasitize the surface of the skin: lice, ticks, bedbugs, some types of flies, mosquitoes. They cause harm to humans through bites and form colonies in the skin, causing skin lesions. Ectoparasites are a serious threat to humans, being carriers of infections and viruses such as encephalitis, malaria, typhoid, plague, and anthrax.
Protozoa
This small parasite in humans, consisting of a single cell and parasitizing in a wide variety of organs and tissues, causes severe diseases, often chronic. The most famous include amoeba, lamblia, and toxoplasma. The routes of entry of parasites are varied, mainly through food and water. Some species cause fatal diseases, such as the aquatic amoeba species Naegleria Fowler, which causes primary amebic meningoencephalitis.
Helminths
A person can be a carrier of many types of parasites. Helminths include types of parasitic worms that live in the internal organs of living organisms. They can be quite large; parasites living in the body can cause significant damage to tissues and organs, and if left untreated, even cause death. There are the following types of parasites in the body:
- Roundworms, nematodes, range from 12 mm (Trichinella) to several tens of centimeters (Ascaris). Some species, such as hookworm, penetrate the skin.
- Trematodes, flatworms, are popularly called flukes because of the suckers on their body. Infection occurs when an invasive form of the parasite enters the body, developing in the body of an intermediate host or in water.
- The largest helminths are cestodes, more commonly known as tapeworms or tapeworms. There are more than 1015 m (bovine tapeworm), and the largest representative, the broad tapeworm, reaches more than 20 m. The intermediate host and source of infection are usually farm animals.
Earthworms
Everyone is familiar with these shiny, curly, reddish-gray tube-shaped earthworm life forms. They are native to Europe, but are now numerous in North America and Western Asia.
The earthworm's digestive system is a tube that runs straight from the mouth, located at the tip of the front end of the body, to the back of the body. Through a special hole, the digested material is transferred outward and leaves the worm's body.
Species differ in their feeding habits, but in general they consume fallen leaves. Living in the soil allows worms to move nutrients such as potassium and nitrogen, which has a beneficial effect on soil properties. Also, the movement of the earthworm creates burrows that facilitate the passage of air and loosen the soil.
What are helminths?
Today, scientists count more than 300 types of various helminthic pathologies that affect the human body. Worms are scientifically called helminths; infectious disease specialists classify them into extraintestinal and intestinal. Depending on the classification of the disease, worms in an adult can be located directly in the intestines or in the liver, lungs and muscles. The most common diseases are ascariasis and enterobiasis.
For information! The presence of helminthic infestation causes oncology and other parasitic diseases.
Enterobiasis
What are the small worms that cause enterobiasis called? Enterobiasis is caused by small worms called pinworms. Their length is no more than 1 cm, one part of the worm is pointed and the other is rounded. The color of pinworms can be white, yellow or black. These worms are nocturnal organisms; worms are known to crawl out of the anus, where they lay their eggs in the folds and die.
For information! The average life span of a pinworm lasts no more than one and a half months.
Ascariasis
Ascariasis is caused by large roundworm worms. Large worms can reach up to 20 cm in length, and their lifespan lasts several years. Such helminths in adults and children parasitize primarily in the small intestine, so they are quite difficult to detect in the feces.
Most common species
The scabies mite causes itchy skin. Common ectoparasites that live on the skin include the scabies mite, lice that cause pediculosis, and the demodicosis mite. In the spring-autumn period, ixodid ticks appear, living in fields and wooded areas, and are called encephalitis ticks. Of the protozoa, the most common types of parasites in humans are Giardia, Toxoplasma, Trichomonas, Coccidia, Amoeba, Babesia, Plasmodium, and Isospora. Common cestodes include bovine and pork tapeworms and the largest wide tapeworm. Among nematodes, roundworms, pinworms, trichinella, and whipworms are often diagnosed. The most common trematodes are strongyloides, opisthorchis, and fasciolas, better known as liver fluke and giant fluke.
Pinworm
Another type of parasite that lives in the intestines is pinworms. These are helminths with a length of 3 to 12 mm. Young children are more susceptible to infection through unwashed food and hands, ingesting worm eggs.
Pinworms
A peculiarity of this type of helminth is the activity of the female, which comes out at night while the person is sleeping. She lays eggs around the anus. The child begins to itch and begins to scratch the itchy organ. At this moment, the larvae attach to the baby’s fingers and under the nails. Helminths can live under a child’s nails for weeks. Re-infection occurs when fingers, where the larvae live, get into the baby’s mouth.
You can cope with pinworms without the use of medications. It is enough to iron the child’s clothes with a hot iron after each nap, dress him in thick underwear to prevent his fingers from coming into contact with helminth eggs, and also cut his nails short so that the eggs cannot linger there. In addition, you need to constantly wash your child’s hands with soap. If it is necessary to use medications, prior consultation with a specialist is required.
Trichinella
Trichinella
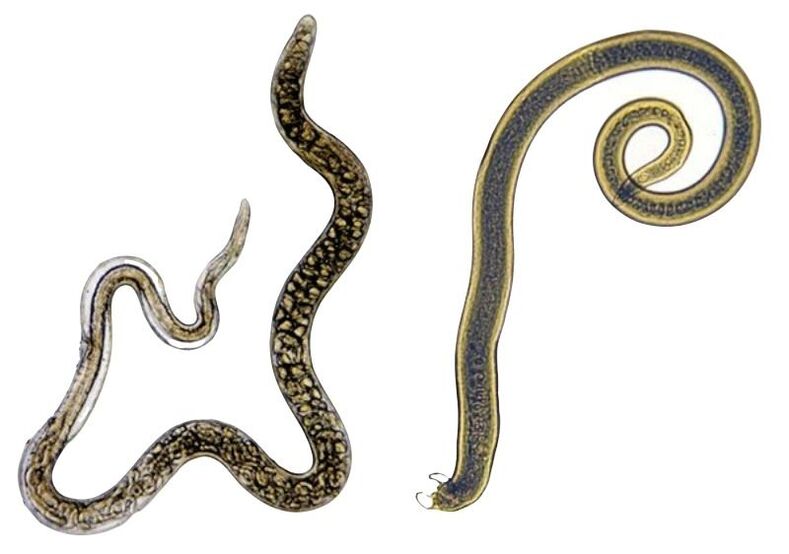

The size of parasitic worms is extremely small, the length of an individual does not exceed 4 mm. They are acquired by eating poorly processed meat containing helminth eggs. Most often it is pork or wild meat. Having undergone thermal procedures with violations, the raw product can provoke infection with these types of helminths.
Parasites can spread very quickly, entering the bloodstream through the intestines. The larvae, traveling inside the body, try to settle in the striated muscles (diaphragm, eye or masticatory muscles). When worm embryos enter the desired part of the body, they create a capsule nearby and can live for many years.
Symptoms of Trichinella infection are muscle pain, swelling of the eyelids and pain when moving the eyes, increased body temperature, puffiness of the face for no reason, swelling of the arms, legs and hands, after a few days all the muscles of the body and joints already hurt, coordination is slightly impaired, a rash appears on the skin. A person is worried about drowsiness or complete insomnia, incessant headaches and stomach upsets.
Tapeworm infections are less common but also occur in both adults and children. Parasites similarly enter the human body at the larval stage and continue their development in the intestines.
Chain
The more common name for such parasitic worms is tapeworm. The bull tapeworm is truly huge and can reach 10 m in length. Small parasitic worm embryos are easily ingested through undercooked or undercooked meat.
The main symptoms of infection are stool disorders, stomach upset, sudden weight loss, vomiting, and lack of appetite. The patient is irritable, suffers from insomnia or sleep disturbances, and dizziness. Children have a delay in general development.
The pork tapeworm is more modest in size, reaching only 2 meters in length. The method of acquisition and the clinical picture are almost the same as above, only a person becomes infected through pork.
Tapeworm
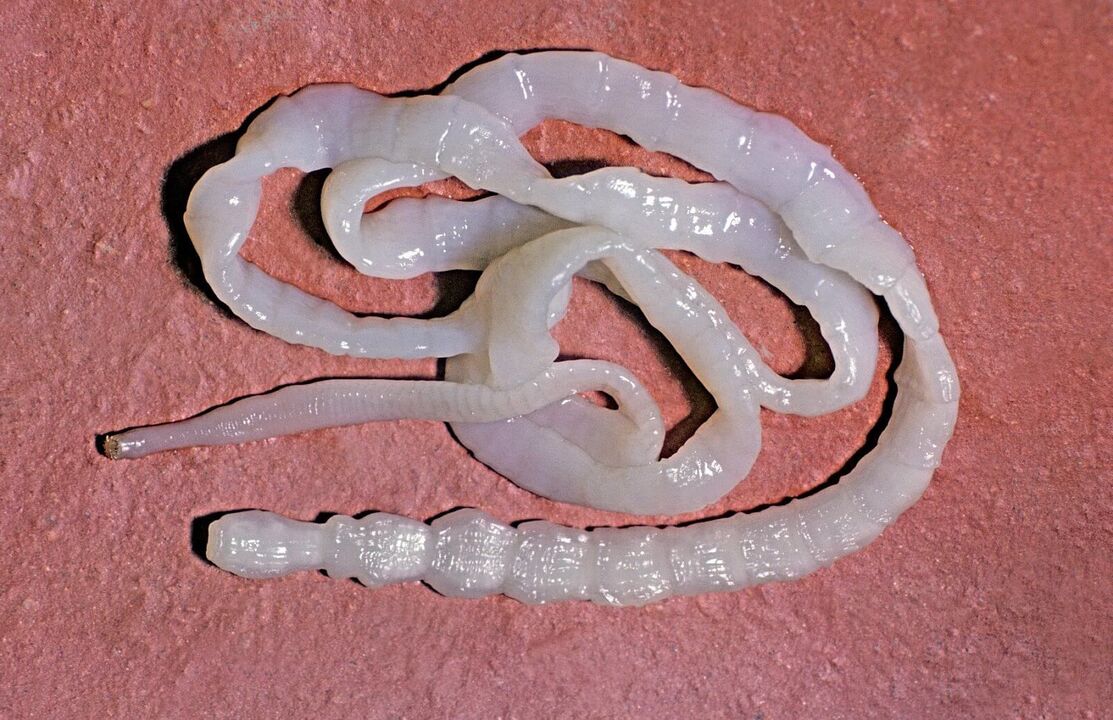

There is another type of tapeworm, the dwarf one. The name was given to it because of its relatively small size; the largest individuals do not exceed 5 centimeters in length. Unwashed hands are more likely to cause the acquisition of parasitic worms. The most common habitats are door handles, lids and toilet seats. Children are at risk for contracting dwarf tapeworm.
After infection with a helminth, the patient experiences abdominal pain, accompanied by nausea, decreased appetite, and weight loss. Dizziness is an integral symptom of infection with almost all known helminths. In this case, seizures resembling epilepsy are not uncommon.
The broad tapeworm is also a subspecies of tapeworm. It has a length from 6 to 15 meters. A person can become infected with helminths through poorly cooked river fish.
A special symptom in this case is red spots on the patient’s tongue, which remind them of pain. In addition, an infected person is worried about: vomiting, diarrhea followed by constipation, constant dizziness and nausea.
Echinococcus
Among all types of helminths, special attention should be paid to such a dangerous one as echinococcus. Any medications are powerless against this parasite, and the patient can only be cured by surgery. Infection, as a rule, occurs through domestic animals with which a person often communicates and caresses.
Thrown into the bloodstream, the worm can settle in any organ, attaching itself and parasitizing inside. The parasite creates a capsule next to itself filled with a liquid composition. There he lives himself and lays out larvae. It is extremely important during the operation to remove it to remove it along with the intact capsule. Otherwise, all organs that receive liquid from the capsule will become infected.
Giardia
Giardia through a magnifying glass
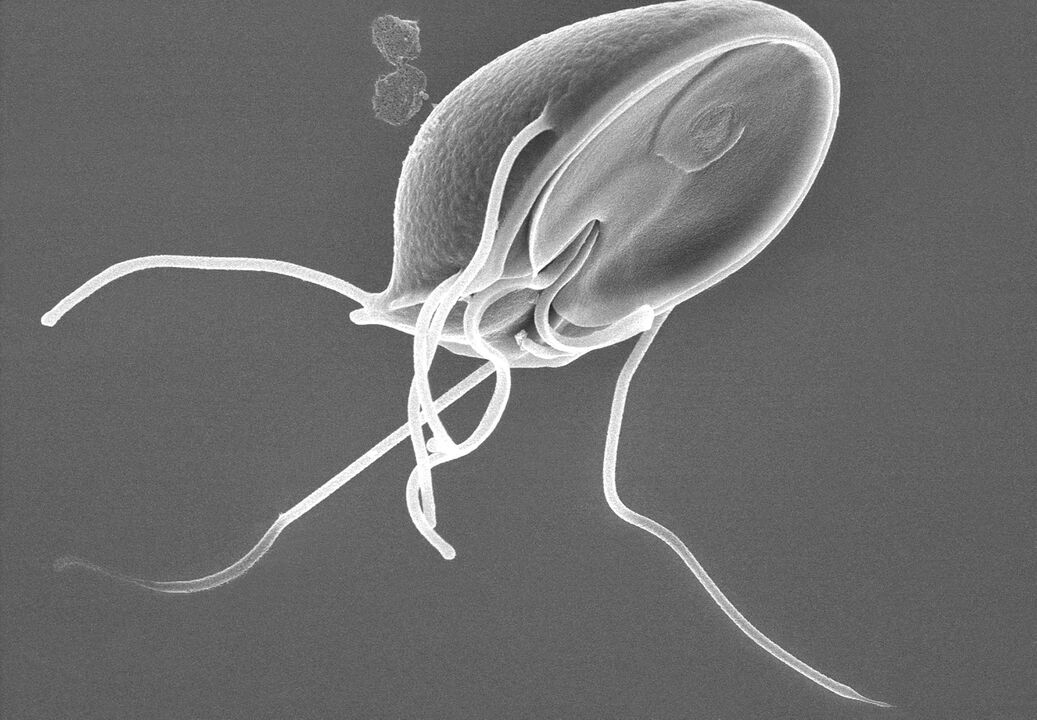
Another type of helminths that are often found in medical practice. Larvae can enter a person through the fecal-oral route if hygiene rules are neglected.
The small intestine becomes the home of the worm. The main symptoms of infection are constant abdominal cramps, nausea, stool disturbances, indigestion, and excessive gas formation. Patients also suffer from nervous disorders, intoxication and allergic reactions.
To defeat worms inside humans, antiprotozoal medications are used, as well as enzymes, choleretic agents and enterosorbents.
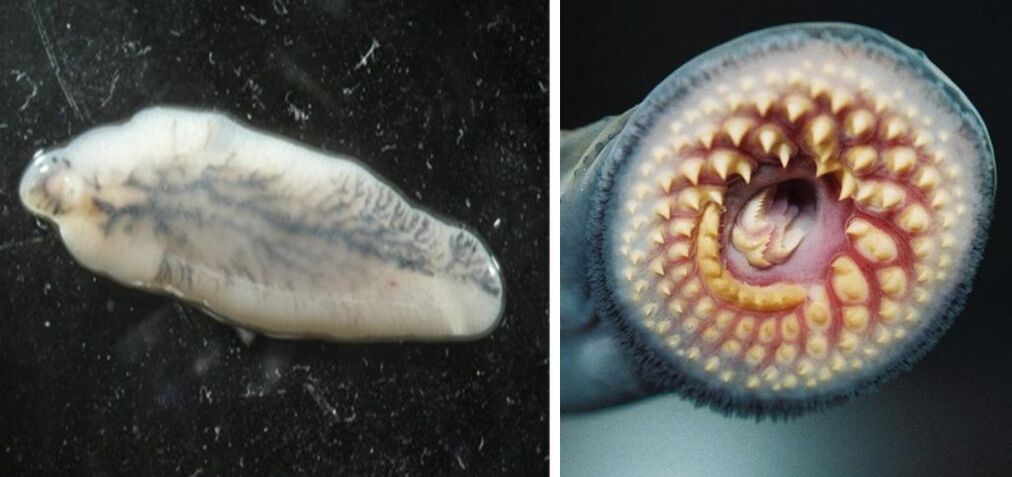
The group of flukes is represented by flatworms, which often infect humanity. Fasciola is the most prominent representative of the group; fluke is no less popular.
Fluke
Parasitic worms are small in size, reaching a length of 413 mm. It penetrates inside a person and settles in the gallbladder or ducts. The worm makes its way inside through not properly cooked frozen or raw river fish.
The clinical picture of fluke infection is expressed by the following signs:
- the temperature rises and lasts for a very long time, without responding to medications;
- painful manifestations in joints and muscle tissue;
- cough;
- skin rash;
- digestive disorders;
- possible jaundice;
- pain in the pancreas.
Fluke

Complications of infection with this type of helminth can be very serious, so you should immediately consult a doctor at the first symptoms of infection. After conducting appropriate research and taking tests, he will prescribe powerful medications that can overcome parasitic worms and expel them from a person.
Fasciola
The gallbladder and ducts of this organ can become a home for helminths. The parasitic worm reaches a length of 37 centimeters. You can become infected through unboiled water or by eating raw algae.
The symptoms of the disease are almost standard: frequent dizziness, feeling tired and unwell, urticaria. The stomach hurts severely and jaundice develops. The disease can take a chronic form.
Schistosoma
Another representative of the group of flukes, a very dangerous type of helminth, is schistosome. You can easily become infected in a pool or in a natural body of water when swimming, as well as after watering garden beds with water that is contaminated with larvae. Whole skin and mucous membranes will not stop the insidious worm; it can get into the body and through them.
The disease, which is caused by parasitic worms, is expressed by itchy skin and elevated temperature to high levels. The chronic stage of the disease can become a complication of such infection. The worm can cause prostatitis in men, as well as colpitis, colitis, ascites and other diseases.
As therapy, strong antiparasitic medications are used that paralyze or destroy parasitic worms, facilitating natural elimination from the body. In particularly advanced cases, aggravated by complications, the surgical method is used.
Remedies for restoring the body after getting rid of parasites
In any case, parasites, by their presence, disrupt the normal functioning of the organs where they were located.
Echinococcus in the kidneys and liver undergoes calcification, roundworms make passages in the lungs and liver that persist even after their death, tapeworms with their suckers damage the intestinal walls, which increases the risk of stomach and duodenal ulcers.
Therefore, traditional medicine recommends using the following recipes to eliminate these consequences:
The intestines are restored by an infusion of flax seeds. The seeds are brewed with boiling water at the rate of a tablespoon per glass and left for 2 hours. Course of treatment: three times a day, 50 ml for a week.
General recovery is achieved by the following collection:
- Nettle leaves 2 parts;
- Rose hips 1 part;
- Rowan fruits 5 parts.
The mixture is brewed with boiling water in the same proportion as the previous point and used in the same way.
Prevention of parasite infestation
Rule No. 1: You cannot eat any fish that is not sufficiently salted, fried or boiled. Sushi, salted herring or sashimi can be considered gourmet food. But essentially it is raw fish, and fish is one of the components of the life cycle of parasitic worms.
How it all happens: first, the larva enters the mollusk, where it does not grow beyond a certain limit, then the mollusk is eaten by a fish, the larva enters its digestive tract, remaining alive, then grows and multiplies, getting into the muscle tissue of the fish, then this fish is eaten by a dolphin, seagullor a polar bear. Or a restaurant visitor who decides to join the high Japanese culture.
In theory, safe raw fish exists. To do this, it must either be frozen immediately after catching and thawed only before cooking, or it must be specially grown on a fish farm with control for the absence of parasites. But it is usually impossible to check whether a risky dish was actually prepared from it.
The same caution must be observed with meat; do not try raw minced meat or freshly salted lard.
In addition, in order not to become infected with helminths, vegetables should be washed before eating, and your hands too. Being a component of the natural environment, these parasites are found to be almost ubiquitous in the human body.
Any contact of food or hands with soil, earth dust and vegetation can leave their microscopic eggs on the food. If they enter the intestines, the eggs will hatch worms, which will not be easy to remove.
There are parasites that attack a person simply passing by or relaxing in nature, such as:
- malarial plasmodium contained in the saliva of mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles,
- the causative agent of encephalitis contained in the saliva of ixodid ticks,
- Gadfly and Wohlfarth fly.
Their prevention involves the use of all kinds of repellents when hiking in the wild, as well as maximum protection of exposed areas of the body (fly nets, nets, special gel).
And in conclusion, it can be noted that following simple rules of hygiene and sanitation, exterminating flies and cockroaches, can significantly reduce the risk of parasite infection, which leads to serious consequences.